As the nation’s largest three-service municipal utility, Memphis Light, Gas and Water (MLGW) serves more than 429,000 customers across multiple counties. The utility strives to deliver electricity, natural gas, and water services that are reliable and affordable.
With a diverse customer base that extends across a range of socio-economic standings, MLGW has worked hard to improve how it communicates with the people it serves.
Limited interactions with customers
The legacy system MLGW relied upon to communicate and engage with its community was clunky and frustrating. Customers would have to call by telephone and wait in a queue to speak directly to a Customer Support representative in order to schedule an appointment.
Once an appointment was booked, there was no system in place to send reminders to customers. As a result, service personnel would show up to attend a call only to find no one at home. On the customer side, the experience was just as frustrating since a missed appointment meant that the customer would have to start the process all over again.
Additionally, without an interactive engagement model, MLGW could not collect feedback from customers immediately following an interaction. The utility was missing out on meaningful data to inform workflows and ensure the customer experience was optimal.
Rising fraud
A fraud scheme on the rise underscored the need to implement a better engagement and communication model.
Scammers acting as MLGW employees would contact customers and threaten to disconnect services without immediate payment. These schemes are often perpetrated in communities where unemployment and other hardships mean a potential disconnection is a genuine possibility.
MLGW wanted its customers to be able to verify that disconnection orders were valid, allowing the utility to protect its communities and eliminate criminal activity.
Moment of Service: a modern, proactive approach

MLGW made customer engagement a critical requirement for all of these reasons. The utility implemented the Mobile Workforce Management (MWM) system from Clevest, an IFS company. The system includes the Customer Communication and Engagement (CCE) feature. Read the case study to understand the scope of the project in its entirety.
The utility created a separate track for the CCE project, building an interactive platform that puts the customer first. The system leverages SMS, IVR, and email so that customers can engage with the utility using their medium of choice.
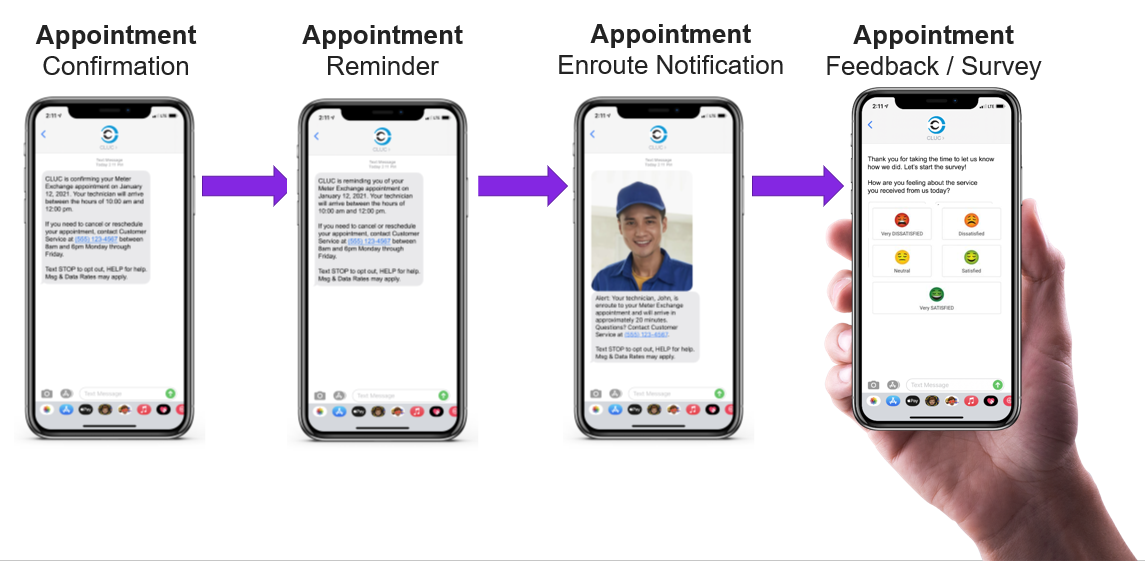
The CCE feature provides configurable and automated capabilities to ensure every customer is aware of a pending service call. When booking an appointment, the system confirms the day and time, including what the customer needs to do if the appointment needs to be changed.
In the lead-up to the service call, additional reminders allow the customer to make adjustments or request a new day or time to accommodate changes in their schedule. The notifications also include a photograph of the technician so the customer knows they are dealing with a validated MLGW technician and not a fraudster.
With such a comprehensive pre-appointment protocol, the technician can arrive ready to work. The customer can also be prepared, stowing pets, and moving any material to provide the technician with easy access.
This automated interaction provides additional efficiencies. For example, once a service call is confirmed, the Clevest MWM platform will automatically schedule work crews and equipment based on the call’s location, date, and time—integrating the new request within the existing work schedules.
Along with a more positive customer experience, MLGW benefits from environmental and cost-saving efficiencies. With no need to attend the same service call multiple times, the utility has eliminated wasted hours and unnecessary truck rolls.
Customer feedback
Feedback can be collected immediately following a call so that input is fresh and reflective of the experience.
Once the utility worker closes the order—based on the job code or the type of work performed—a personalized, conversational survey is sent via the customer’s preferred medium. The survey questions align with the nature of the service call.
Since the surveys are easily configurable, MLGW can make adjustments to focus on specific points in the customer experience. For example, the utility may want to confirm with the customer that the technician followed safety protocols and arrived wearing regulated equipment such as a facemask, shoe guards, and gloves. Alternatively, the utility may focus on the interaction between the technician and the customer to confirm the work was carried out politely and professionally.
All survey results are logged and aggregated to show overall CSAT scores. If negative feedback is received, the system will intuitively present additional questions so MLGW can collect the details it needs to drive improvements and deliver better service to its customers.
Customer safety
The new communication capabilities also increase safety and security for customers when it comes to fraud scams.
With a two-way, interactive communication model, customers know in advance when a worker is coming. If someone knocks at their door or calls them asking for payment, the customer can reach out and validate that the contact is genuine.
By coupling existing measures such as social media outreach with the new system which includes photo identification for all workers, MLGW reduces exposure to this type of fraud, ensuring its customers are protected.
What’s next
The Clevest MWM system with CCE capabilities has elevated how MLGW connects with its customers. This flexible platform allows the utility to optimize how it interacts, proactively monitoring service levels while reducing emissions and operating costs.
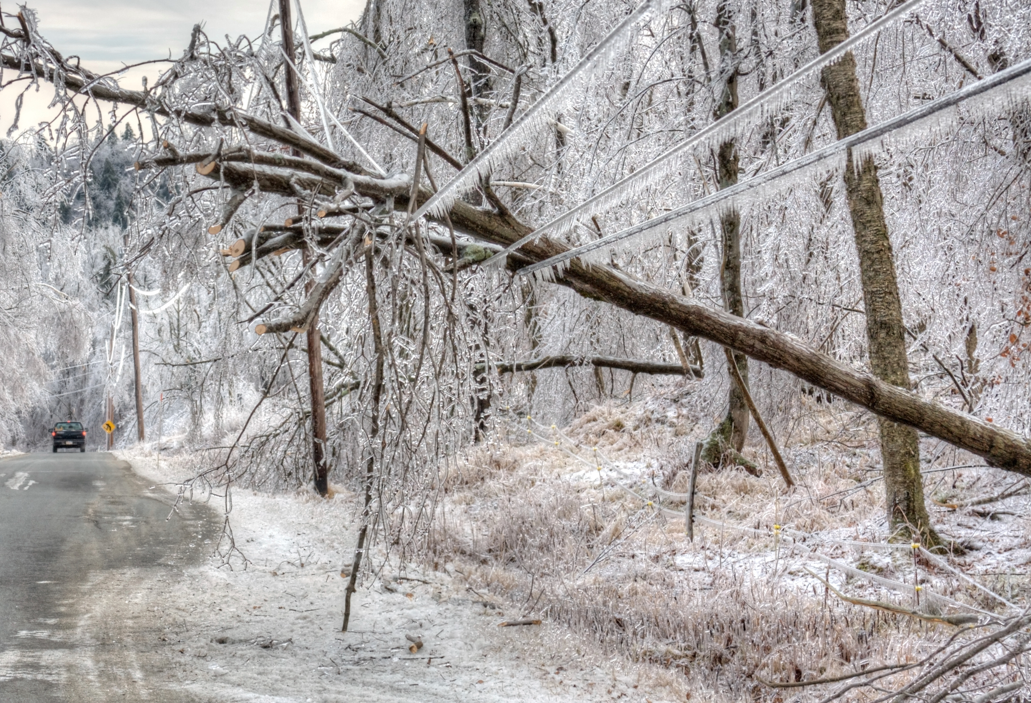

The next phase of the project focuses on mass outage notifications to customers when an emergency occurs. In early 2021, this is exactly what happened when a rare snowfall wreaked havoc in Memphis, creating a water crisis that broke water mains across counties. The utility was challenged to communicate effectively with customers, providing updates and other critical information such as boil water advisories.
The incident reinforced the need for the utility to validate email addresses and differentiate between landline and mobile phone numbers. With updated contact information, MLGW can ensure it has capacity to communicate effectively with all of its customers during an emergency—across all supported mediums. Most importantly, the communication model will be two-way, allowing the utility to leverage its customer base as a reporting tool on the ground.
In tandem with the mass outage notification strategy, the Clevest MWM platform will automate coordination in the field. The technology will provide alerts and activate field crews to respond to the emergency, emphasizing worker safety while resolving the situation.
With real-time communication and scheduling, emergency response efforts will be timely and more effective, safeguarding people, property, and the environment. Read the entire case study to learn more.